If you want to print something on a 3D printer it is necessary to have a digital 3D model. The model is prepared in a 3D modeling program (CAD software) or by scanning that is suitable for organic shapes such as a human figure. If you are not familiar with the software, there are many model databases listed below or you can use our CAD service (we can help you to prepare a model).
3D programms
TinkerCAD
Great web-based modeling app for all those, who are just starting with 3D design and modeling. Moreover you have access to database of models made by other users.
www.tinkercad.com
123Dapp
Several excellent apps for beginners, mobile apps and database of models.
www.123dapp.com
SketchUp
One of the most widespread and most commonly used programs which is very simple and intuitive to use. It is especially popular among architects and plenty of tutorials are available. Its disadvantage is that export to .STL file format buggy models with lots of open edges.
www.sketchup.com
Blender
Most sophisticated open-source 3D software with a lot of features suitable for challenging projects.
www.blender.org
Databases of 3D models
Thingiverse
Perhaps the most popular database of models for 3D printing. It provides recommendations how to print a model or how to adjust it.
www.thingiverse.com
Yeggi
Metas engine that searches through many databases at once.
www.yeggi.com
Turbosquid
Database of model addressed not only for 3D printing but also for animation and visualisation. It contains a lot of models that are free of charge.
www.turbosquid.com
MyMiniFactory
Similar concept like the more famous Thingiverse. They guarantee that all models are printable.
www.myminifactory.com
3D design and printability of model
When designing a model or parts for additive manufacturing (- 3D printing), it is always necessary to think about their manufacturability. As with any production technology, – 3D printing has its own principles which you must be aware of in order to benefit from its full potential.
First of all you need to know the purpose of the model what you expect from it and thus to select the optimal material and technology . Each one has its advantages but also the limits.
6 principles of good 3D design
1. Material properties
It is necessary to know whether the model is only for presentation
(i.e., – we only care about its shape) or whether we expect certain mechanical properties such as strength, flexibility, hardness, heat resistance and etc.
Material features can affect the wall thickness, orientation in the printer and layer height.
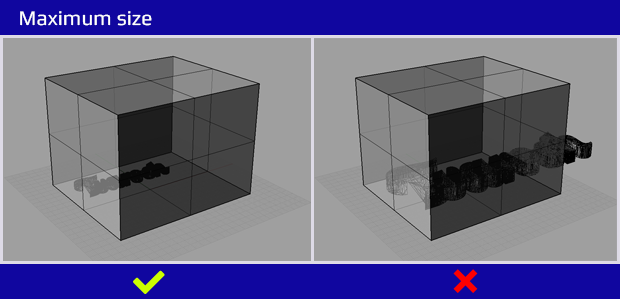
2. Size of the model
Each machine and technology has its maximum size or volume that can be printed. However models can be divided into smaller pieces, printed separately and then bonded together.
Maximum bounding box that we can arrange is with SLA technology 2100 x 700 x 800 mm.
3. Wall thickness
minimal wall thickness (depending on technology is 0,5 – 2 mm)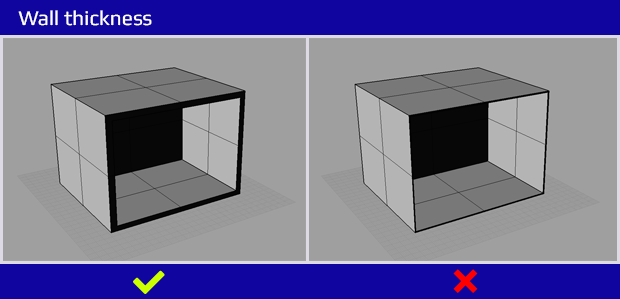
4. Level of detail
Each technology has its limitations in terms of displayed size of the minimum detail. It depends mainly on layer height and “thickness of tool” (laser or nozzle).
5. Layering and Infill
3D printing make it possible to set various layer heights and in FDM technology also amount of infill. This affects material properties, level of detail and the total price.
| |
low layer height |
less amount of infill |
| time |
increase |
decrease |
| surface finish |
increase |
decrease |
| mechanical features |
increase |
decrease |
| level of details |
increase |
decrease |
| price |
increase |
decrease |
6. Proper file format and its flawlessness
No matter which application is used, in the end, it is necessary to properly export the creation for 3D printing. The most common format supported by most 3D programs is .STL (StereoLithography).
The surface of the models created in this format is composed of bigger and smaller triangles or diamonds – polygons. These are positioned next to each other so that they create the desired shape (a polygon mesh).

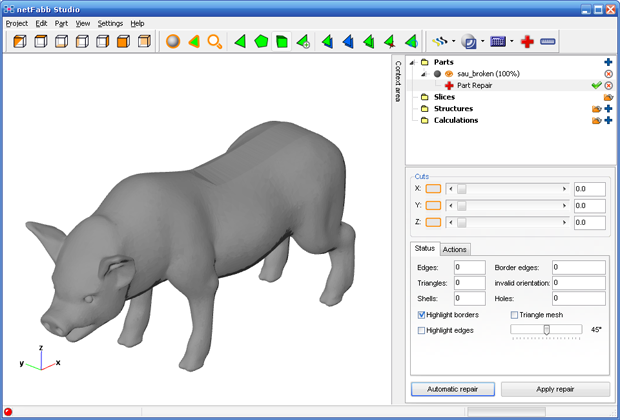
Exporting the final model in various types of software (3ds Max, Maya, Blender, etc.) often creates a flaw in the polygon mesh, which can cause problems with printing. This mainly due to the fact that these programs were mainly designed for animation and creating visualisations. It is therefore important to check the exported files and sometimes make corrections. For this step we recommend Netfabb.
Netfabb
It is one of the most widely used programs which can eliminate flaws and prepare the model for printing. There is a paid and a free version, the difference primarily being in functionality. This software is available for Windows, OS X and Linux.
If you don’t want to install it, you can also find a web application. After uploading the file, it will be repaired on the servers and can then be downloaded back. This application is good for one-time users, when only a few files need to be checked.
The most common flaws and defects in models (in the polygon mesh)
Non-manifold edge – edges of polysurfaces or meshes that have more than two faces joined to a single edge are non-manifold. 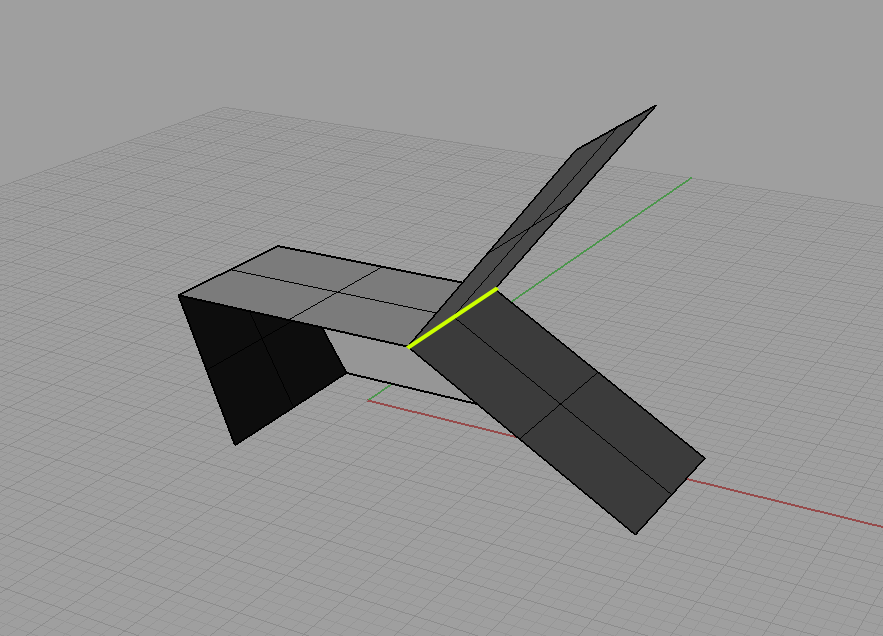
Non-manifold point – when two surfaces meet at one point but do not share an edge.
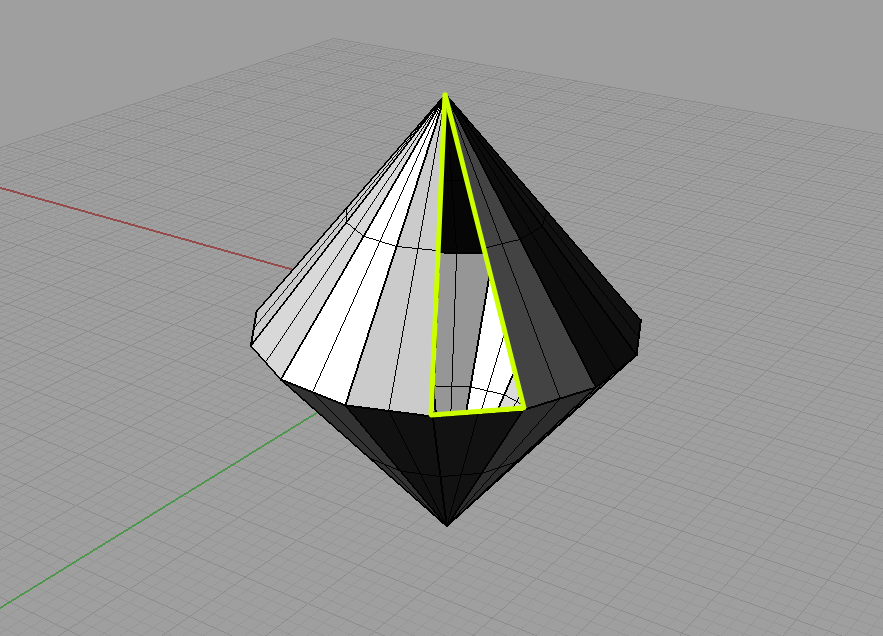
Naked edges, border edges – each edge of a surface needs to be connected to another edge. If that is not the case, there will be holes in the model surface.
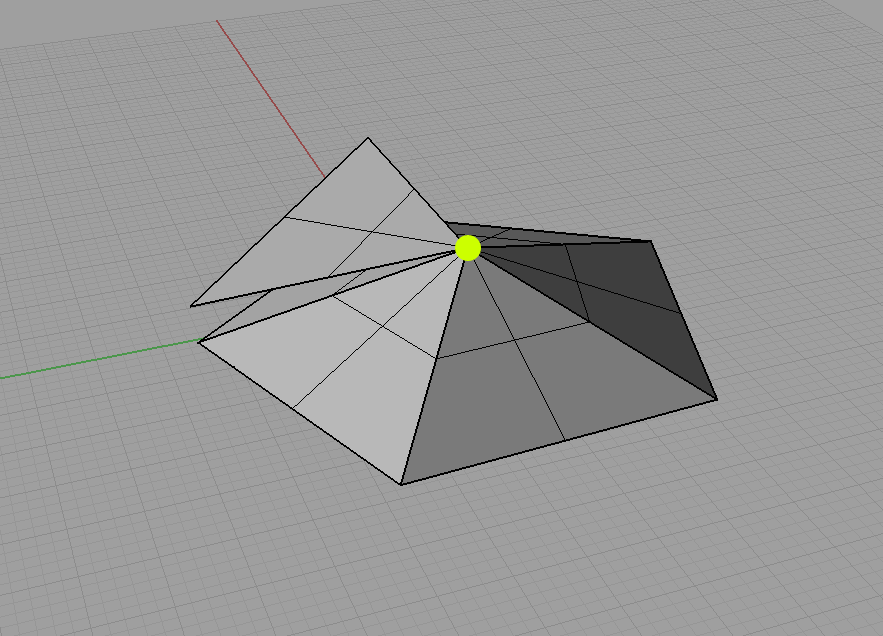
Separate enclosed surfaces (solids) share a common edge – similar to non-manifold edge, but the difference is that not more than two surfaces but more than two enclosed objects are meeting at one edge. There needs to be some space between them.
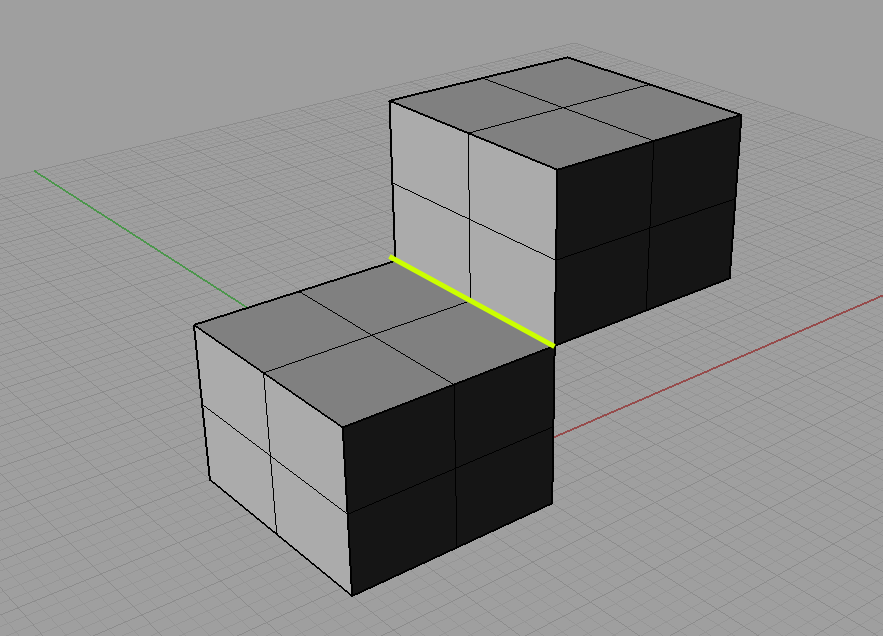
Overlapping surfaces (self-intersecting) – the surfaces are cutting through each other or they’re sticking out from the surface field of the model.
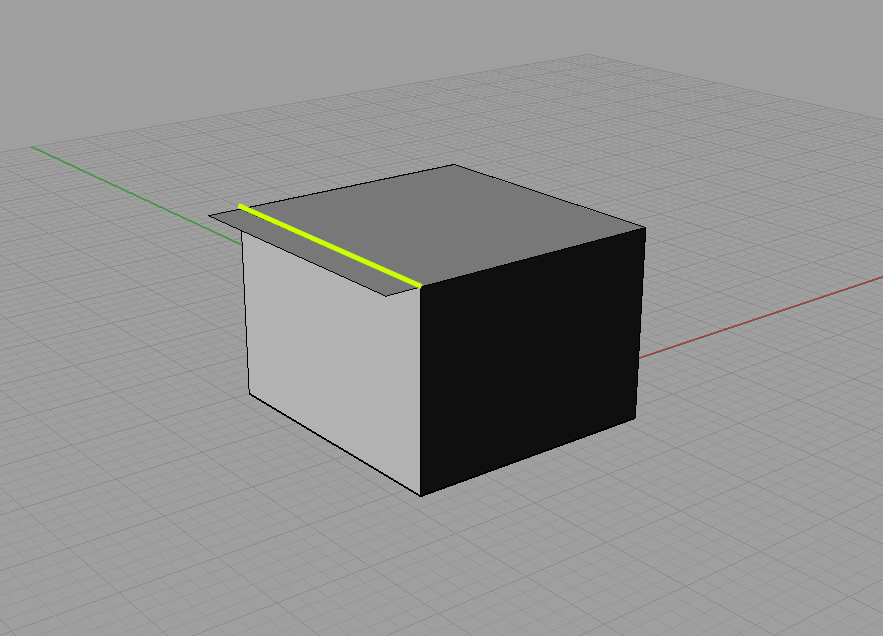
Normals orientation (solid orientation) – with every surface we distinguish two orientations – in and out. To enable printing, all the surfaces must face the same direction. No matter which direction they are facing, they just need to be the same.
If you have problem to prepare the model for printing properly you can contact us via e-mail info(at)tvaroch.sk
Where to go? Make model | Industrial Design












